Electronic Components Supplier | Transformers, Inductors, Inverters
PRODUCT PARAMETERS
Description
Overview of Metal Induction Heating Furnace
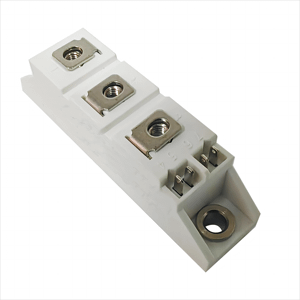
Thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device composed of four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials. It functions as a bistable switch, conducting current only when triggered by a gate signal, and remains conducting until the voltage across it drops below a certain threshold. Thyristors are widely used for controlling high-power electrical circuits, offering efficient and reliable performance in various industrial and electronic applications.
Features of Metal Induction Heating Furnace
- High current and voltage handling capabilities
- Low on-state voltage drop, reducing power loss
- Fast switching speeds for precise control
- Latching behavior: once triggered, remains conducting without continuous gate signal
- Robust and durable design suitable for harsh environments
- Available in various types (e.g., SCR, TRIAC, GTO) for specific needs
(Metal Induction Heating Furnace)
Specifications of Metal Induction Heating Furnace
This heating system heats up metal utilizing electrical energy. It creates a magnetic field. The metal goes inside this field. This makes the metal warm up fast from the inside. The furnace works for many metal types. It thaws steel, copper, light weight aluminum, and others.
The power modifications based on what you need. Little heating systems begin around 15 kW. Huge commercial heating systems look at 1000 kW. The frequency matters as well. Low frequencies work best for large items. High regularities heat small components quicker. Common frequencies are 1 kHz, 3 kHz, 10 kHz, and greater.
Temperature control is precise. It easily reaches over 1800 ° C (3272 ° F). This is warm enough to thaw most metals. Melting rate depends upon the steel and the heater dimension. A tiny heater might melt a couple of kgs in minutes. A big heater melts loads per hour.
The crucible holds the metal. It is made from strong materials. These materials take care of severe heat. Usual selections are graphite or unique ceramics. The coil borders the crucible. Water streams with the coil. This keeps the coil cool throughout operation.
The heater requires good cooling. A chiller system provides this. It distributes cool water. The water flows through the coil and other warm components. This stops getting too hot. The control panel is simple. Operators set the power and temperature. They view the procedure. Digital presents reveal the present temperature level and power degree.
Safety attributes are very important. The furnace has automated shut-off. This happens if the water circulation quits. It also takes place if the temperature obtains too high. Emergency situation quit buttons are easy to reach. Operators put on safety equipment. This gear protects against warmth and dashes. The heater design avoids unexpected call with real-time components.
(Metal Induction Heating Furnace)
Applications of Metal Induction Heating Furnace
Metal induction home heating furnaces warmth metal quickly and specifically. They utilize magnetic fields. This method works for many commercial jobs. Metal gets hot promptly without straight call. This saves energy. It also maintains the work environment cleaner.
Building shops make use of these heaters a whole lot. They heat up metal items before forming. The heat is even throughout the metal. This makes forging less complicated. It also makes the final product more powerful. Regular heating is key for good forgings.
Melting metal is an additional big use. Factories melt scrap steel or alloys in induction heaters. Thawing occurs fast. You shed very little metal throughout melting. Operators control the temperature exactly. This is very important for making certain alloys.
Warmth treatment needs exact temperature control. Induction heaters do this well. They harden the surface of steel components. Think about equipments or shafts. The core stays tough. The tough surface area withstands wear. This expands the component’s life. Annealing and tempering additionally use induction warm.
Steel joining usages induction home heating as well. Brazing and soldering requirement managed warmth. Induction heats up the joint area quick. The base steel doesn’t get too hot. This makes solid, tidy joints. Production lines utilize this technique usually.
Putting parts together securely makes use of shrink fitting. Induction heats up the external part swiftly. The metal broadens. You fit the great internal part inside conveniently. The external part cools and reduces. This creates a very limited, strong hold. It’s faster than old oven techniques.
Company Profile
PDDN Photoelectron Technology Co., Ltd. is one of the leading enterprises in power electronics technology and power products, which is fully involved in developing solar inverters, transformers, voltage regulators, distribution cabinets, thyristors, modules, diodes, heaters, and other electronic devices or semiconductors. We will be committed to providing users with high-quality, efficient products and considerate service.
It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union, and Paypal. PDDN will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by sea, or by air. If you want high-quality Metal Induction Heating Furnace, please send us inquiries; we will be here to help you.
Payment Methods
L/C, T/T, Western Union, Paypal, Credit Card etc.
Shipment
By sea, by air, by express, as customers request.
Storage Conditions
1) Store in a dry environment at room temperature.
2) Avoid damp and high temperature.
3) Use immediately after opening the inner packing bag.
5 FAQs of Metal Induction Heating Furnace
Here are five common questions about metal induction heating furnaces:
How does an induction furnace heat metal?
It heats metal using magnets and electricity. Electricity flows through a special copper coil. This creates a strong magnetic field inside the coil. Put metal inside this field. The magnetic field makes electric currents flow inside the metal itself. These currents fight the metal’s natural resistance. This fight makes heat. The metal gets hot very fast.
What makes the heating speed different?
Several things change how fast the metal heats. The metal type matters. Steel heats differently than aluminum. The furnace power level is important. More power heats faster. The metal size and shape affect speed. Thick pieces take longer. The coil design influences the heating pattern. Some designs focus heat better. The frequency of the electricity also changes things.
How is the temperature controlled?
We measure the heat. Special tools watch the metal temperature. Common tools are infrared pyrometers. These tools look at the metal and see its heat level. They send this information to the furnace control system. The control system adjusts the power. It sends more electricity to get hotter. It sends less electricity to cool down. This keeps the metal at the right temperature.
How is the furnace kept cool?
The furnace parts get hot too. We need to cool them. Water cooling is the main method. Cold water moves through pipes inside the copper coil. The water takes the heat away. Other parts might need cooling. Power supplies and capacitors need cooling. Sometimes we use air fans. Sometimes we use special coolants. Good cooling protects the furnace.
Can it heat any metal?
It heats many metals well. It works best on metals magnets like. Iron and steel heat very efficiently. Many other metals work too. Copper, brass, and aluminum can be heated. Some metals are harder to heat. Non-magnetic stainless steel heats slower. The metal’s shape matters. Simple shapes heat evenly. Odd shapes might heat unevenly. The furnace setup needs adjusting for different metals.
(Metal Induction Heating Furnace)
REQUEST A QUOTE
RELATED PRODUCTS
Digital Control SCR Voltage Regulator Speed Control Dimmer Thermostat

Regulator for Controlled Rectifier Circuit Thyristor Manufacturing Wind Generators and Resistance Welders Companies

High Quality Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) Thyristor Module for Resistance Welders Understanding the Working Principle
Disc Type Fast Switching Thyristor / fast SCR / fast Thyristor
3 Phase Thyristor Regulator 220v 480VAC SCR Power Regulator Voltage Controller